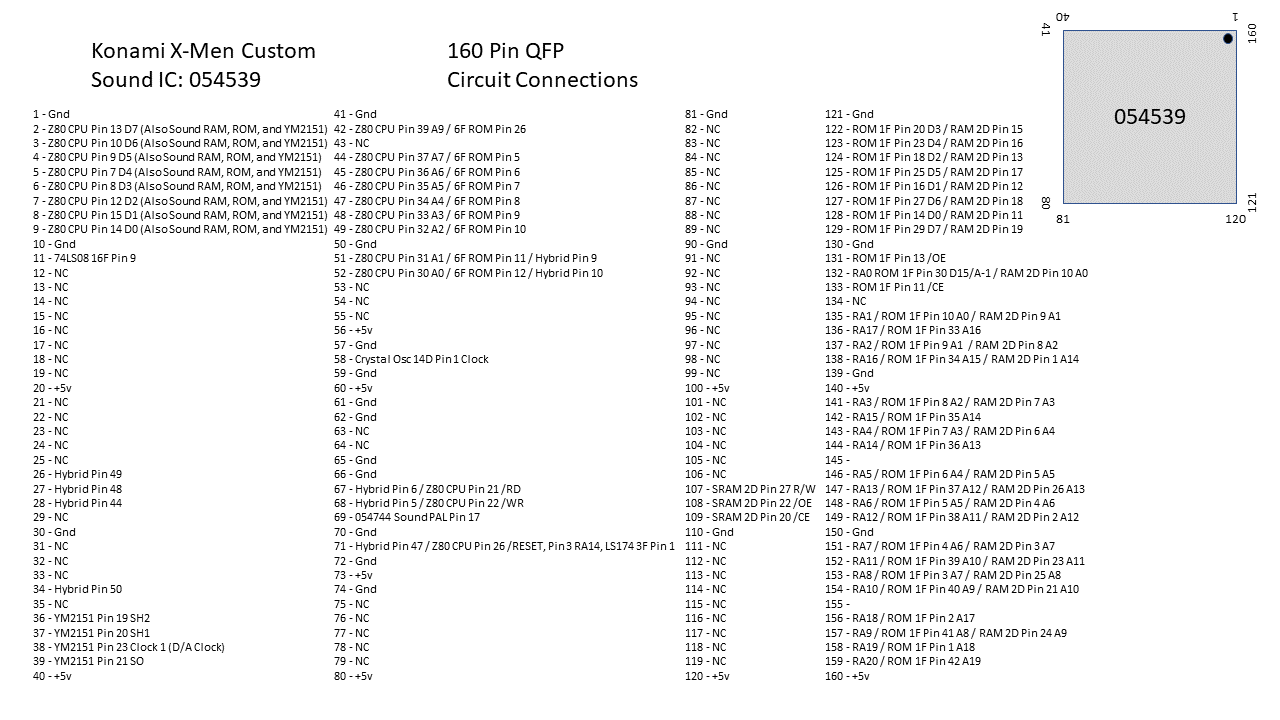
Last Updated: 4/24/2024
This tutorial is a straightforward procedure for using a colorimeter to calibrate an arcade cab or consumer CRT. Using a colorimeter is perfect for people that want their displays calibrated to a high standard with no “eyeballing it” or guesswork involved.
Display color calibration in a nutshell is precisely matching the contrast, brightness and colors of a video display against a reference standard such that (A) the calibrated display looks the same as other calibrated displays and (B) subtle details in video games aren’t missed due to either color washout (white point too high) or black crush (black point too low).
Up front, here’s some vocabulary words that this tutorial uses:
- White Point: The measurement of the brightest white your monitor can display.
- Black Point: The measurement of the darkest shadow your monitor can display.
- Contrast: Adjusts the White Point of the RGB color guns equally.
- Brightness: Adjusts the Black Point of the RGB color guns equally.
- Gain or Drive: Individually adjusts the White Point of each Red, Blue and Green color gun.
- Cutoff or Bias: Individually adjusts the Black Point of each Red, Blue and Green color gun.
- Color Temperature: Expressed in kelvins, color temperature is a parameter comparing the color of a light source (ie your display or a light bulb) against an real-world reference light source (ie the sun). Lower color temperatures (< 3000 K) are considered “warm” (red or yellowish) while higher color temperatures (> 5000 K) are considered “cold” (blueish).
- The abbreviation for 6500 kelvin color temperature is D65 while the abbreviation for 9300 kelvin is D93.
Note that display color calibration is a VERY deep rabbit hole with a lot of information, detail and nuance. This guide is intended for enthusiasts that just want a procedure they can quickly step through to make their displays look nice. There’s much more you can do in addition to what I’ve written up here if you want to be very precise with your display’s calibration.
If you want to delve deeper into the world of color calibration, consider these resources and articles:
- Calibration channel on the RetroTechUSA Discord
- RetroRGB Colour Malarkey
- Wikipedia: Color Temperature
- Wikipedia: NTSC Colorimetry
- HCFR Calibration – Custom Coordinates
- ConsoleMods CRT Color Calibration Guide
- CurtPalMe Grayscale Color Calibration for Dummies
This tutorial steps you through a white point balance procedure for your display, but does not cover adjustment of the RGB primary and secondaries since adjustments to those are very specific to each CRT model. Geometry adjustment is also not covered here.
Necessary Calibration Components
- Laptop or desktop Windows computer to run the Colorimeter
- Colorimeter to accurately read color measurements off the display
- Pattern Generator to push accurate calibration images to the display
- Calibration Software that reads the values from the Colorimeter and displays them to you in a readable format
What I Use
- X-Rite I1 Display Pro colorimeter – it’s around $30 – $100 used from Ebay.
- MiSTer FPGA with MiSTercade add-on running HCFR core Pattern Generator and SNES 240P Test Suite – Download Link
- Other good choices for a Pattern Generator are:
- 240P Test Suite running on a game console
- PGenerator running on a Raspberry Pi
- PGenerator is a great pattern generation option since it supports 15 khz output for CRTs and the laptop you’re using to read measurements can control it automatically, but it is tricky to setup for the first time. There is an excellent YouTube tutorial by StickFreaks available here: https://youtu.be/D6z0wS5oRoE
- DVD player running the FreeCalRec601 disc
- HCFR – the same program that interfaces with the colorimeter – if the display you’re calibrating supports an output resolution that your HCFR PC supports.
- HCFR calibration software
If applicable, use a color generator that matches what will be connected to your display the most often – ie, if you’ll be running a MISTer FPGA in an arcade cab, use a MiSTer as your color generator.
White Point Reference Selection
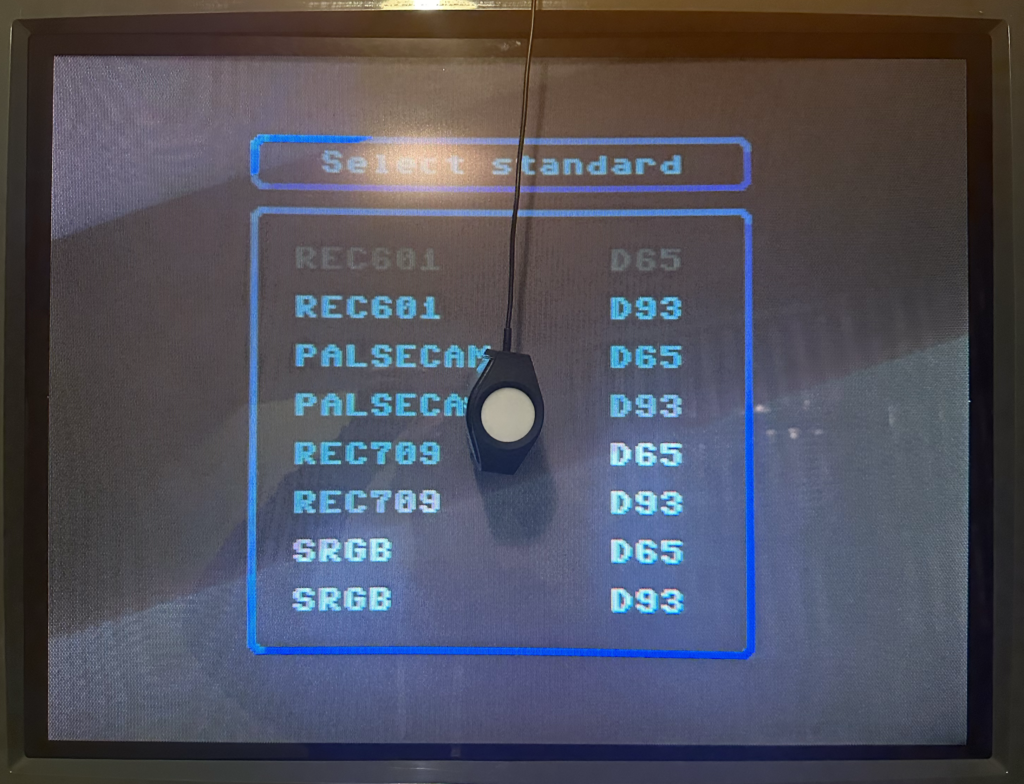
One decision you should make before you start is the white point standard you want your display calibrated against.
For retro video games, there are two target white point standards to consider:
- D65 is considered the standard that US CRTs were calibrated for in the 80s-90s. It is a “warmer” white point and thus the display will have stronger red output.
- D93 is considered the standard that Japanese televisions were calibrated for in the 80s-90s. Is is a “cooler” white point and thus the display will have a stronger blue output.
- Choosing one or the other is a personal preference.
Personally, I go with D65 for displays with US tubes (ie Zenith, RCA, Magnavox) and D93 for Japanese tubes (Sony, Toshiba, Panasonic, JVC, Hitachi) - There’s a thorough writeup on D65 vs D93 here: https://www.retrorgb.com/colour-malarkey.html
Procedure
These instructions assume you’re using HCFR as your colorimeter interface software on your Windows laptop.
One-time only software setup
1) Download and install the free HCFR software from here:
https://sourceforge.net/projects/hcfr/files/
2) Launch HCFR.
3) Click on the Advanced menu and choose Preferences.
4) Click on the References tab. Set the settings as follows:
| D65 White Point | D93 White Point | Advanced Tab |
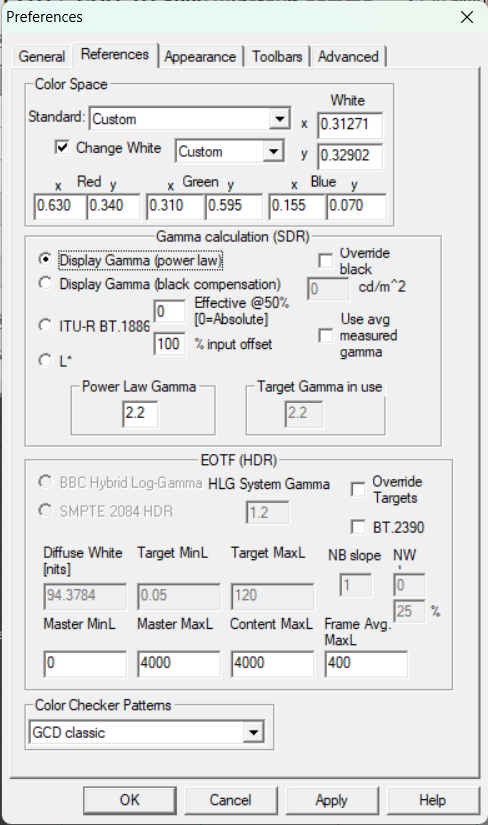
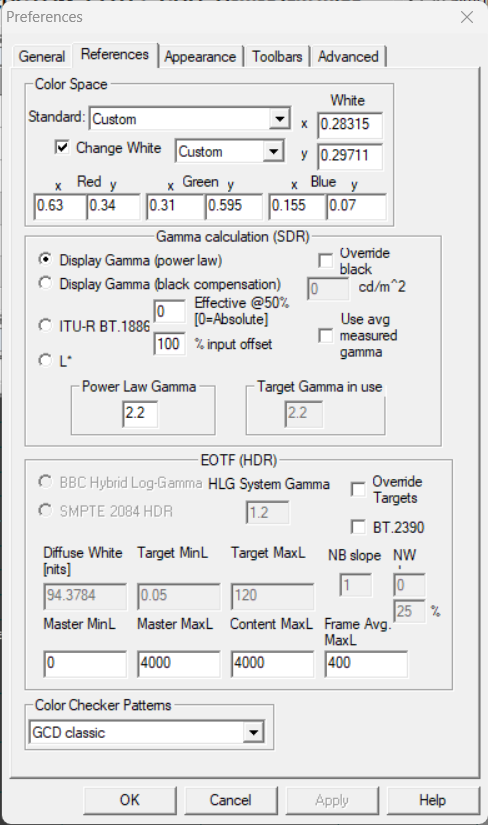
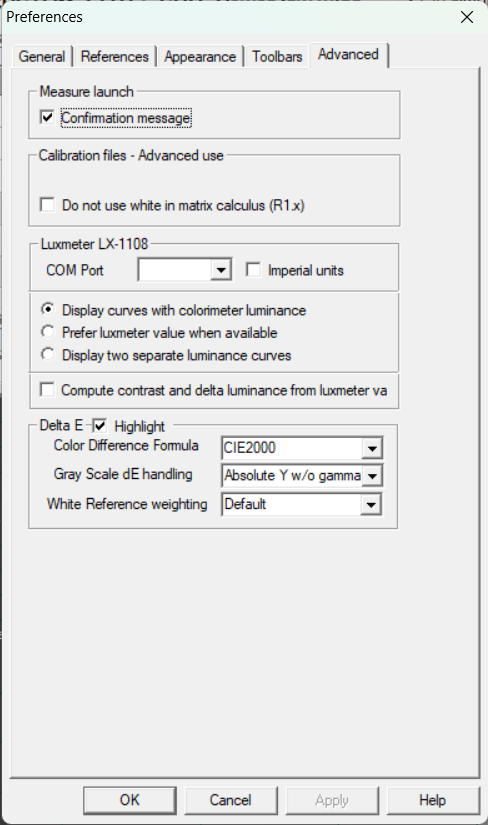
6) Click OK to close the Preferences window.
Technical Note: the values entered for the Red, Green and Blue references in HCFR correspond to the SMPTE-C phospher specification. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NTSC#Colorimetry and HCFR Calibration – Custom Coordinates
Calibrating a display
IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT TERMINOLOGY
CRT manufacturers often confuse the labeling for Contrast, Brightness, Drive and Cutoff.
“Contrast” is the term for adjusting the White Point level.
“Brightness” and “Black Level” are two interchangeable terms for the Black Point adjustment. I use “Brightness” in this guide, but yours may be labeled “Black Level”.
“Drive” and “Gain” are two interchangeable names for the upper-end Red, Green and Blue color gun adjustments. I use “Drive” in this guide, but yours might be labeled Gain.
“Cutoff” and “Bias” are two interchangeable names for the low-end Red, Green and Blue color gun adjustments. I use “Cutoff” in this guide, but yours may be labeled Bias.
CRT and colorimeter setup
1) Connect your test pattern generator to the display.
2) Power on the display. Display a 100% solid white test pattern.
In the 240P Test Suite, go to “Test Patterns” -> “White Screen”.
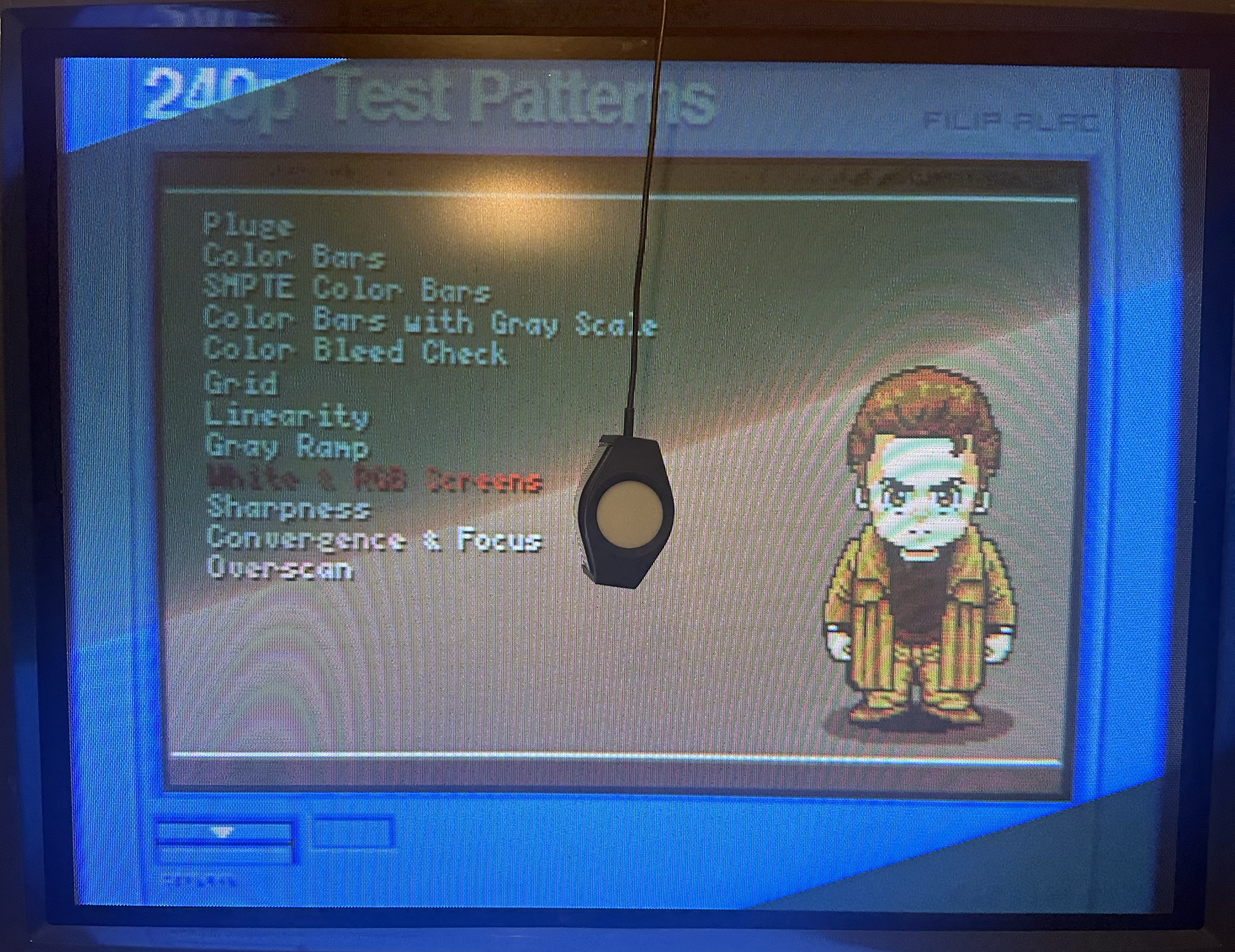

3) Wipe down the monitor glass with glass cleaner. Place the colorimeter directly on the glass in the center of the screen. Place a book or something heavy on top of the cable to stop it from sliding or falling off the screen.
4) Wait one hour with the screen on all-white to let the CRT and chassis warm up.
5) Connect the colorimeter to your laptop running HCRF with the USB cable. Launch HCRF.
6) Click on the “File” menu and choose “New”.
7) On the Generator Selection screen, choose:
- DVD manual: if you’re using a pattern generator that can’t be controlled from the laptop, such as MiSTer HCRF core, 240P Test Suite or a DVD Player.
- Automatic: if the laptop is the pattern generator and thus connected to the cab display as a secondary monitor.
- PGenerator will also be detected and used by HCFR when Automatic is selected.
8) Select your model of Colorimeter from the sensor list, select “Do not use a meter correction file” and click Finish.
9) Your meter might now ask what kind of display you’re calibrating – choose “CRT” or “Refresh Display”. Also, Reading Type should be set to “Display”. Click the Calibrate Meter button. Some meters will then ask you to display a white image of 80% IRE or higher. You’re already displaying a 100% IRE all-white screen, so just click OK to finish the calibration.
10) In the main HCFR window that appears, click on the Green Triangle button in the menu bar to start taking readings.
Adjustments – Ideally, you’ll want to do this with the room as dark as possible.
Flyback Screen Dial – Initial Approximate Calibration
Source: https://emphatic.se/?p=710
Archived Copy: PDF
NOTE: If you don’t have straight-forward access to your CRT’s flyback, set each Drive, Cutoff, Contrast, and Brightness setting to the center position and move on to the next section.
1) Set the CRT controls as follows:
- Each RGB Drive: All the way down.
- Each RGB Cutoff: Center position.
- Contrast: Center position.
- Brightness: Center position.
2) Display a white grid pattern.
In the 240P Test Suite, go to “Test Patterns” -> “Grid”.
3) Turn the Screen dial on the flyback down (counter-clockwise) until the display is completely dark and pitch black. You want to go just past the last trace of the grid.
4) Turn each RGB Cutoff up until you see the black space around the white grid turn into the color you’re adjusting. Then turn it down until the black is perfectly black again.
5) Turn each RGB Drive up until the grid is really white without bleeding out / turning blurry.
Now the CRT is broadly dialed in, we can fine tune the adjustment using the colorimeter.
Contrast and Brightness – Precise Calibration Part 1
Source 1: https://consolemods.org/wiki/CRT:CRT_Color_Calibration_Guide
Source 2: http://www.curtpalme.com/forum/viewtopic.php?t=10457
Archive: PDF
1) Display a 100% IRE test pattern.
In the MiSTer HCFR core, choose “REC601 D65” or “REC601 D93” from the menu depending on which white point standard you’re using. Up and Down on the controller will cycle the IRE level up or down in 10% increments.
In the 240P Test Suite, back out and go to “Test Patterns” -> “100 IRE”. Depending on the console, some control buttons will adjust the IRE level up or down in 10% increments.
2) Click on the 100 Column in HCRF. If the colorimeter isn’t currently taking readings, click on the green Triangle button in the upper-middle of the toolbar.
The “Y” measurement tells you how bright your screen is. Typically, you want it at 100 nits. If you plan to always run your display in a dark setting, you may want to go down to either 95 or 90.
Adjust the SubContrast dial (if you have one; Contrast otherwise) until the Y readout hits your target.
- If your chassis doesn’t have any Contrast adjustment dials or if you can’t get the Contrast to go high enough to hit your target, try adjusting the Red, Green and Blue Drive/Gain pots evenly upward.
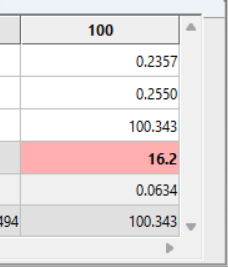

3) Click on the 20 Column in HCRF. Change your pattern generator to display a 20% IRE test pattern.
4) Your target now for the Y value is 0.3% of the reading at IRE 100.
So if 100 nits is your IRE 100 target, 3.0 is what you want Y to read at IRE 20.
HCRF also calculates the target value for you – look at “Y Target”.
Adjust the SubBrightness dial (if you have one; Brightness otherwise) until the Y readout hits your target.
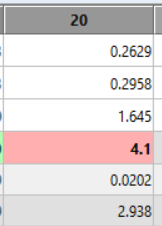
The Y Target reads 2.938.

If you can’t go low or high enough try adjusting the Red, Green and Blue Cutoff pots evenly.
- Note that aged chassis components and tubes may have trouble hitting these high and/or low targets. In that case, just get as close as you can.
5) When you change Brightness, it affects Contrast and vice-versa, so repeat Steps 2-4 until the Brightness and Contrast are balanced against each other with the appropriate Y target for each.
Drive and Cutoffs – Precise Calibration Part 2
1) Click on the 80 Column in HCRF. Change your pattern generator to display a 80% IRE test pattern.
2) Look at the gauges in the lower-left corner of HCFR. The Red, Green and Blue gauges show your levels relative to the target, while the yellow gauge shows your Delta E (deviation) away from the target. As the RGB gauges get close to 100%, the Delta E gauge will drop. Your goal is to get Delta E as close to zero as possible.
Adjust the Blue and Red Drive pots until the gauges are as close to 100% as possible and Delta E is as close to 0 as possible. Adjust Blue first before Red.
Adjusting Green will scew both the Red and Blue levels, so you shouldn’t touch the Green pot unless you can’t get Red or Blue to adjust far enough to reach your targets. You’ll notice as you adjust the Red and Blue levels closer to 100%, the Green will be pulled there as well.
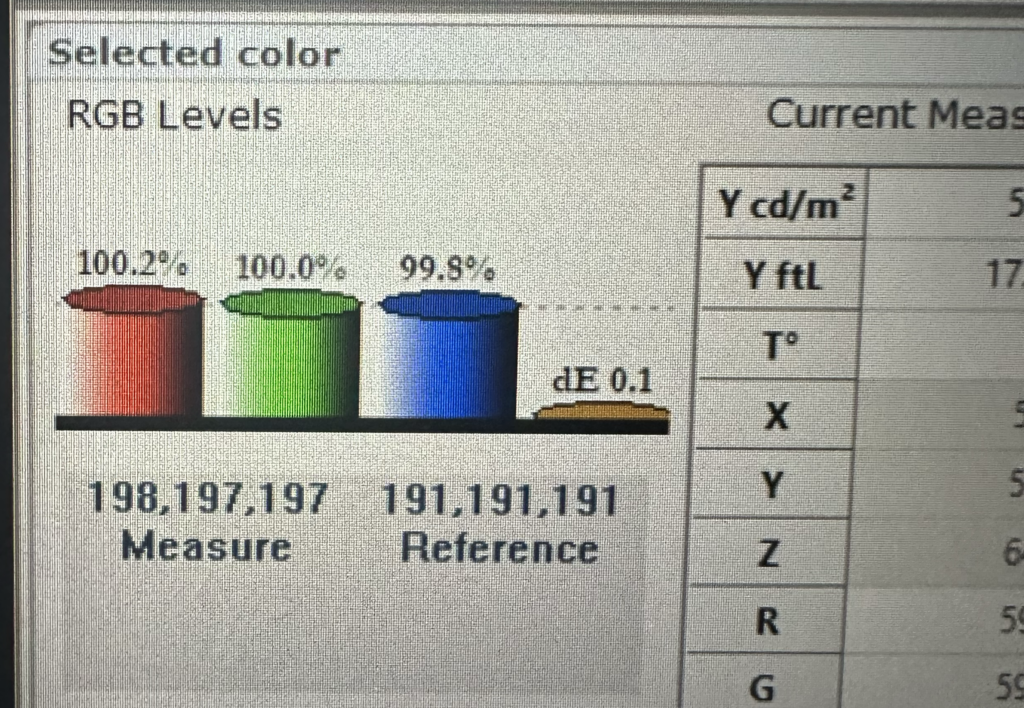
3) Click on the 20 Column in HCRF. Change your pattern generator to display a 20% IRE test pattern.
4) Adjust the Blue and Red Cutoff pots until the gauges are as close to 100% as possible. Adjust the Blue first before Red.
Adjusting Green will scew the Red and Blue levels, so you shouldn’t touch the Green pot unless you can’t get Red or Blue to adjust far enough to reach your targets. You’ll notice as you adjust the Red and Blue levels closer to 100%, the Green will be pulled there as well.
5) When you change the Drive pots, the Cutoff target shifts and vice-versa, so repeat Steps 1 – 4, going back and forth between 20 and 80 IRE and adjusting Cutoff and Drive respectively until both of them are as close to 100.0% RGB and 0.0 Delta E readings as possible on the gauges.
Now, the display is pretty well dialed in at this point, but if you’re extra picky, repeat the Part 1 – Contrast and Brightness steps one more time, because adjusting the Drive and Cutoffs will have shifted those values a little bit. If you do end up readjusting Contrast and Brightness, you’ll also have to readjust the Drive and Cutoffs again afterward as well, but none of them will need very much readjustment.
Verifying the White Balance Calibration
If you’d like to check your cab CRT now and see how the White Balance calibration holds up across the gamma range, do the following:
1) In HCFR, click the Green Triangle to stop taking constant readings.
2) Click the Measures menu and choose “Gray scale”, and click Yes at the prompt.
3) The software will prompt you to “set 0% grey level”. Set an IRE 0% test pattern on your generator.
In 240P Test Suite, use the L and R buttons on the controller to set IRE to 0, and click OK.
4) After a moment, the software will now prompt to “set 10% grey level”. Set an IRE 10% test pattern on your generator.
In 240P Test Suite, use the L and R buttons to set IRE to 10, and click OK. Repeat all the way up through the 10 incrementing IRE levels.
5) When the measurement is complete, look at the DeltaE row. Recall that DeltaE measures your variance from the perfect white balance target. If all ten cells are green (Delta E < 2.0) then you’re in good shape – your white balance is approximately on-par with a professional CRT. If some or all of the cells are yellow (Delta E between 2.0 and 3.0) then you’re approximately on par with a consumer CRT. If some or all of the cells are red (Delta E > 3.0) then you’re off target – either the calibration is wrong, your chassis PCB needs servicing, or the color guns in your tube are worn out.
Also, with Gray Scale selected from the drop-down in the upper-left corner, make a note of your Average Gamma and your Contrast Ratio. Ideally, you want an Average Gamma of 2.2 and an Average Contrast Ratio of at least 1000 : 1, but your results will vary based on tube and chassis age, specs, etc.
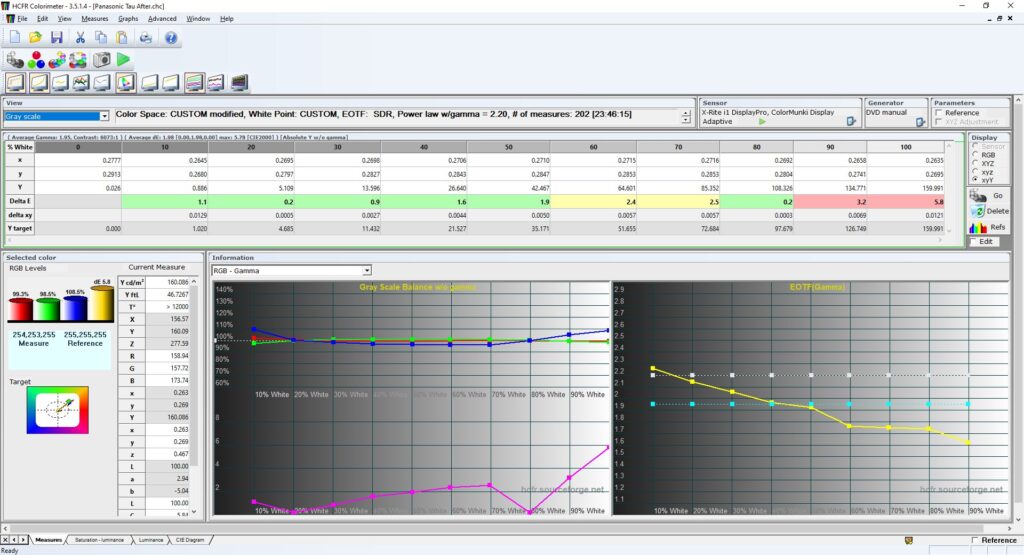
Note that calibration drifts as the tube and caps age – you may want to “tune up” your calibration every couple of years.
Post-Calibration Examples






This tube is worn and has burn-in and poor black levels